In a groundbreaking development that could reshape the landscape of medical technology, Neuralink, the brain-computer interface company founded by Elon Musk, has successfully conducted human trials involving seven patients. These trials have yielded remarkable results, demonstrating the potential of Neuralink’s N1 chip to restore mobility and communication for individuals suffering from severe disabilities.
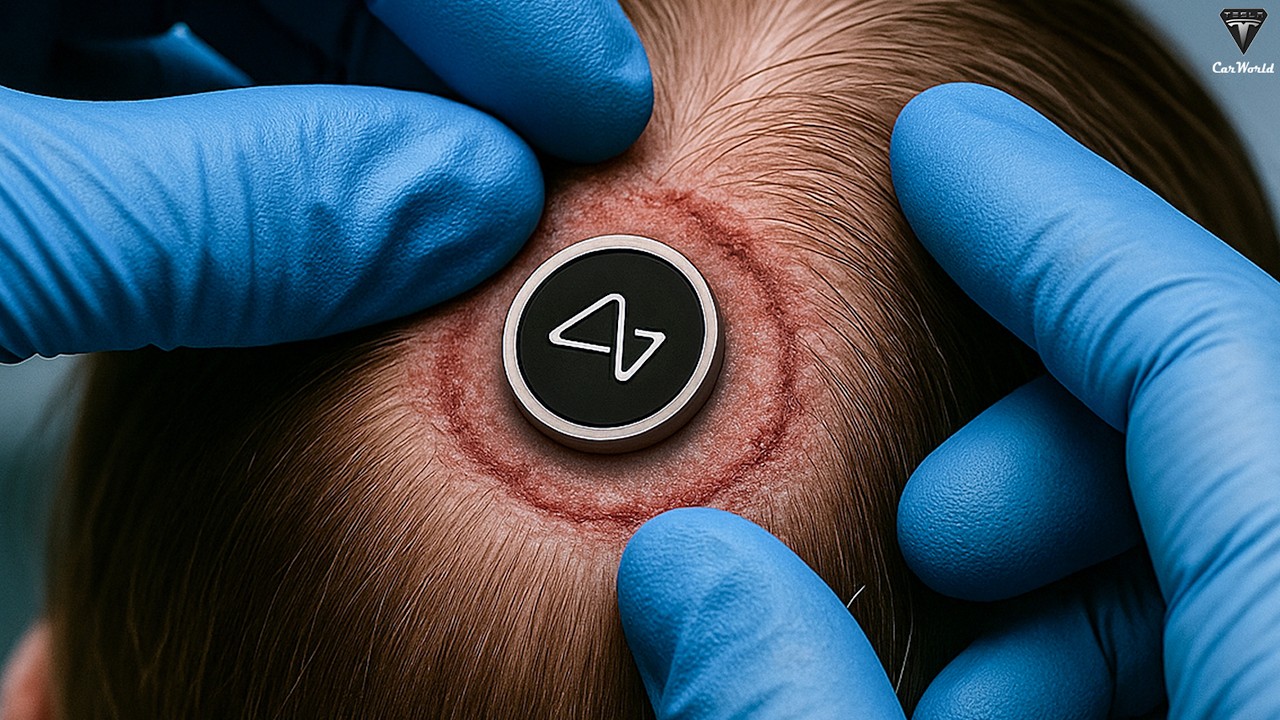 During a recent presentation, Musk unveiled the transformative capabilities of the N1 chip, which allows users to control computers and other devices using only their thoughts. This technology aims to assist those with paralysis and neurological disorders, offering new hope for independence and improved quality of life. Among the patients is Noland Arba, a quadriplegic who has achieved extraordinary feats, including controlling a computer cursor at a record-breaking speed of nine bits per second and playing video games solely through mental commands.
During a recent presentation, Musk unveiled the transformative capabilities of the N1 chip, which allows users to control computers and other devices using only their thoughts. This technology aims to assist those with paralysis and neurological disorders, offering new hope for independence and improved quality of life. Among the patients is Noland Arba, a quadriplegic who has achieved extraordinary feats, including controlling a computer cursor at a record-breaking speed of nine bits per second and playing video games solely through mental commands.
The implications of this technology extend beyond mere mobility. Musk announced ambitious future projects, including “Blind Sight,” which aims to restore vision to individuals who have never seen, and advanced speech decoding to enable direct thought-to-speech communication for those with ALS or other speech impairments. These initiatives are expected to begin trials within the next two years.
Neuralink’s trials, conducted primarily at the Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix and the University of Miami, have shown that the N1 chip remains stable, with participants averaging 50 hours of use per week. This level of integration into daily life underscores the device’s potential for real-world applications, fostering greater independence for users.
As Neuralink accelerates its research and expands its patient recruitment efforts, the company is poised to challenge existing perceptions of disability and redefine the capabilities of individuals with severe mobility limitations. The promise of merging human cognition with advanced technology has never been more tangible, raising questions about the future of human enhancement and the ethical considerations that accompany such innovations.